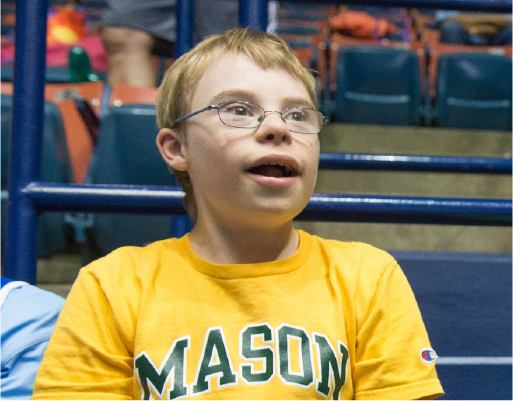
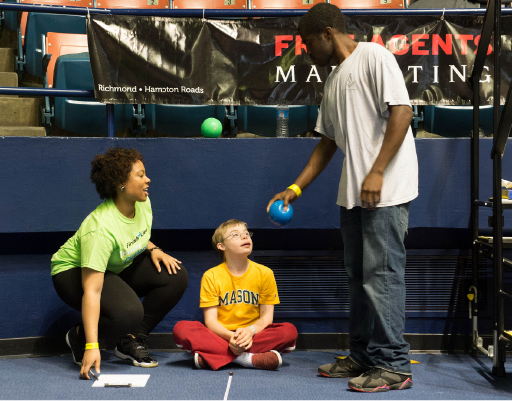Our Athletes
Course Modules
Start Course
| Module 1 | Module 1 |
| Unit 1 | Welcome to Special Olympics |
| Unit 2 | What Makes Special Olympics Different? |
| Unit 3 | Our Athletes |
| Unit 4 | Being a Sports Assistant |
| Unit 5 | Assessment |
| Unit 6 | Sport: Level 1 Sport Assistant Course Evaluation Survey |
Powered By WP Courseware
Module Summary
Introduction
In this topic you’re going to learn about the most important part of Special Olympics: our athletes. We’ll talk about intellectual disability, how those with intellectual disabilities can participate in sport, and our approach to fitness.

What is intellectual disability?
Here is the World Health Organisation’s definition:
“Intellectual disability means a significantly reduced ability to understand new or complex information and to learn and apply new skills (impaired intelligence). This results in a reduced ability to cope independently (impaired social functioning), and begins before adulthood, with a lasting effect on development.”
How can you best support athletes with intellectual disabilities to play and develop in sport?
We want to understand the needs of our athletes to help us to better support them during sport. To help do this, we’ve created a quick reference coaching guide to help you when working with athletes who display various different behaviours. The guide suggests strategies and solutions for behaviours that are commonly associated with intellectual disabilities. In fact, you will see many of these behaviours with any athletes you might coach, whether or not they have ID.
Obviously, all of our athletes are individuals with their own likes and dislikes, so it’s important that you get to know them. Their families, caregivers, teachers and coaches can all tell you more about the athlete. Don’t forget though, that the best way to get to know your athletes is to spend time with them, talking to them and asking them about their interests, likes and dislikes.
Here’s an example of how the reference guide can help you.
What is fitness?
Our athletes’ fitness is very important to us. Special Olympics defines fitness as:
The state of optimal health and functional ability (movement) as a result of:

Physical Activity

Healthy eating habits

Adequate hydration
The components
This component displays an image gallery with accompanying text. Use the next and back navigation controls to work through the narrative.
All of our sport training sessions have the same key components, these examples should give you a good idea of what they involve.
Your turn
Now that you’ve learned what they involve, it’s your turn to plan a session. Pick one of your favourite sports and imagine that you’re creating a training session for it. You need include a warm-up, review of previously learned skills, new skills/drills, competition style practice/scrimmage, and a cool-down and review of session.
Remember, you can always refer to the above for inspiration.
Top tips
So how do you take responsibility for health and safety? Here are some tips:
-
Check for hazards – are there trip hazards, poorly maintained pieces of equipment etc?
-
Eliminate or reduce any risks – always play it safe.
-
Make sure you know the emergency plan and your role within it.
-
There should be a first aid provider present at all times.